记录常见的 激活函数 以及 损失函数
激活函数
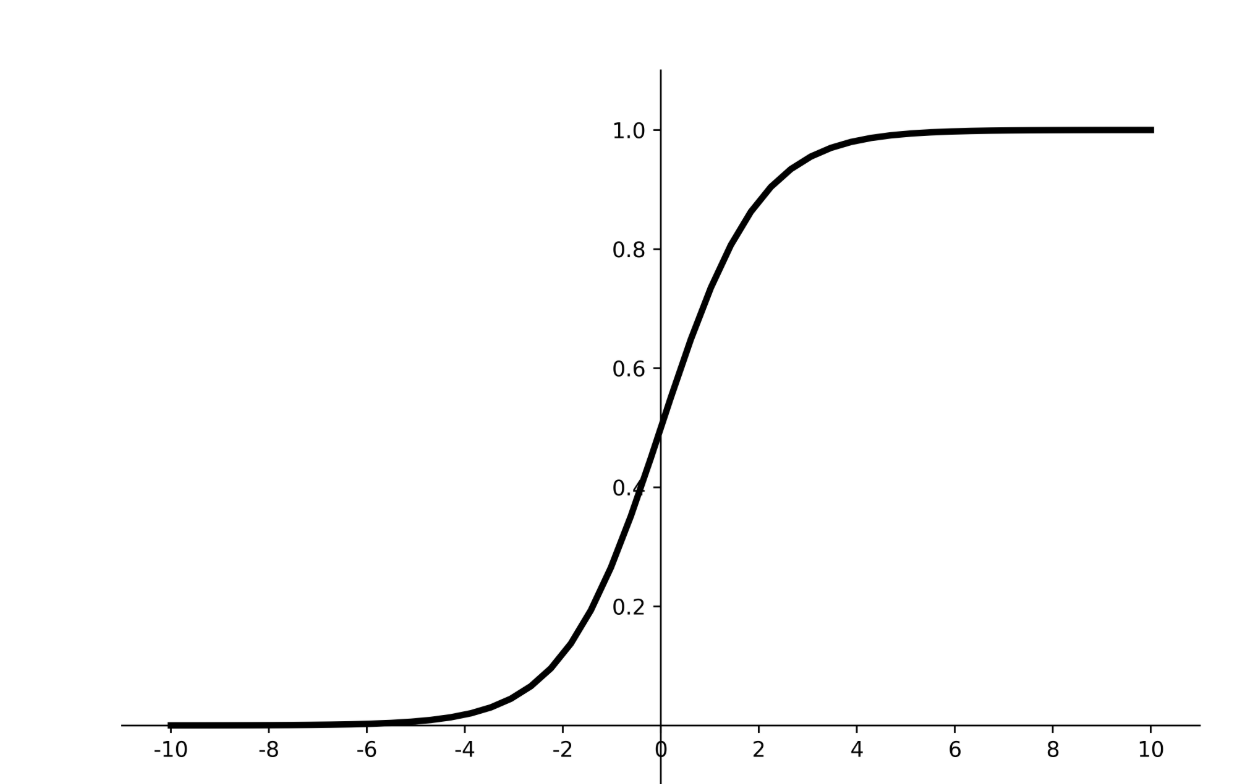
Sigmoid
f(x) = 1/(1+e^(-x))
$$ f(x)=\frac{1}{1+e^{-x}} $$
f(0) = 0.5 ,f(x) 取值范围在 (0,1) 之间
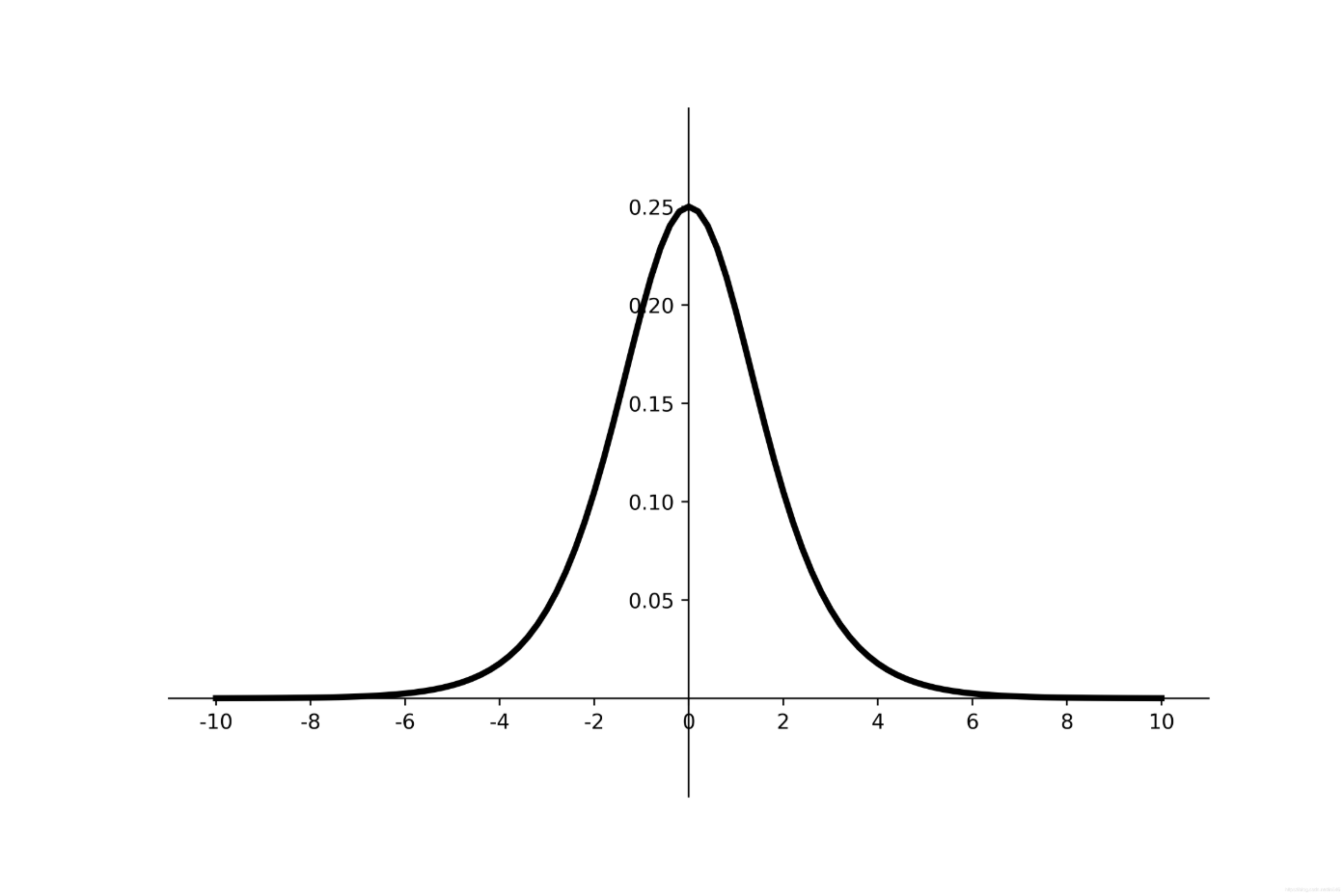
导数为:
f'(x) = f(x) - (1-f(x))
$$ f’(x)= f(x) - (1-f(x)) $$
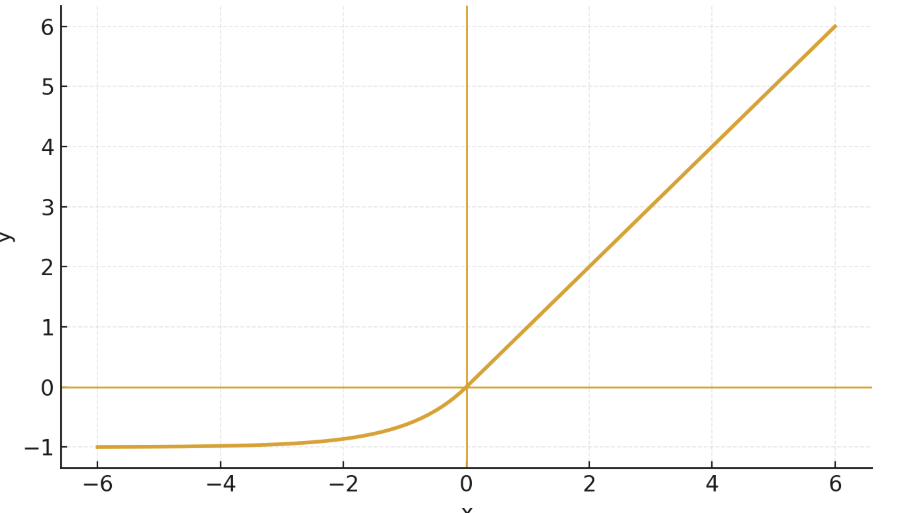
图像如下:
优点: 1、 输出映射在(0,1)之间,单调连续,输出范围有限,优化稳定,可用作输出层; 2、求导容易。 缺点: 1、易造成梯度消失; 2、输出非0均值,收敛慢; 3、幂运算复杂,训练时间长。
sigmoid 只适用于二分类问题,不适用于多分类问题
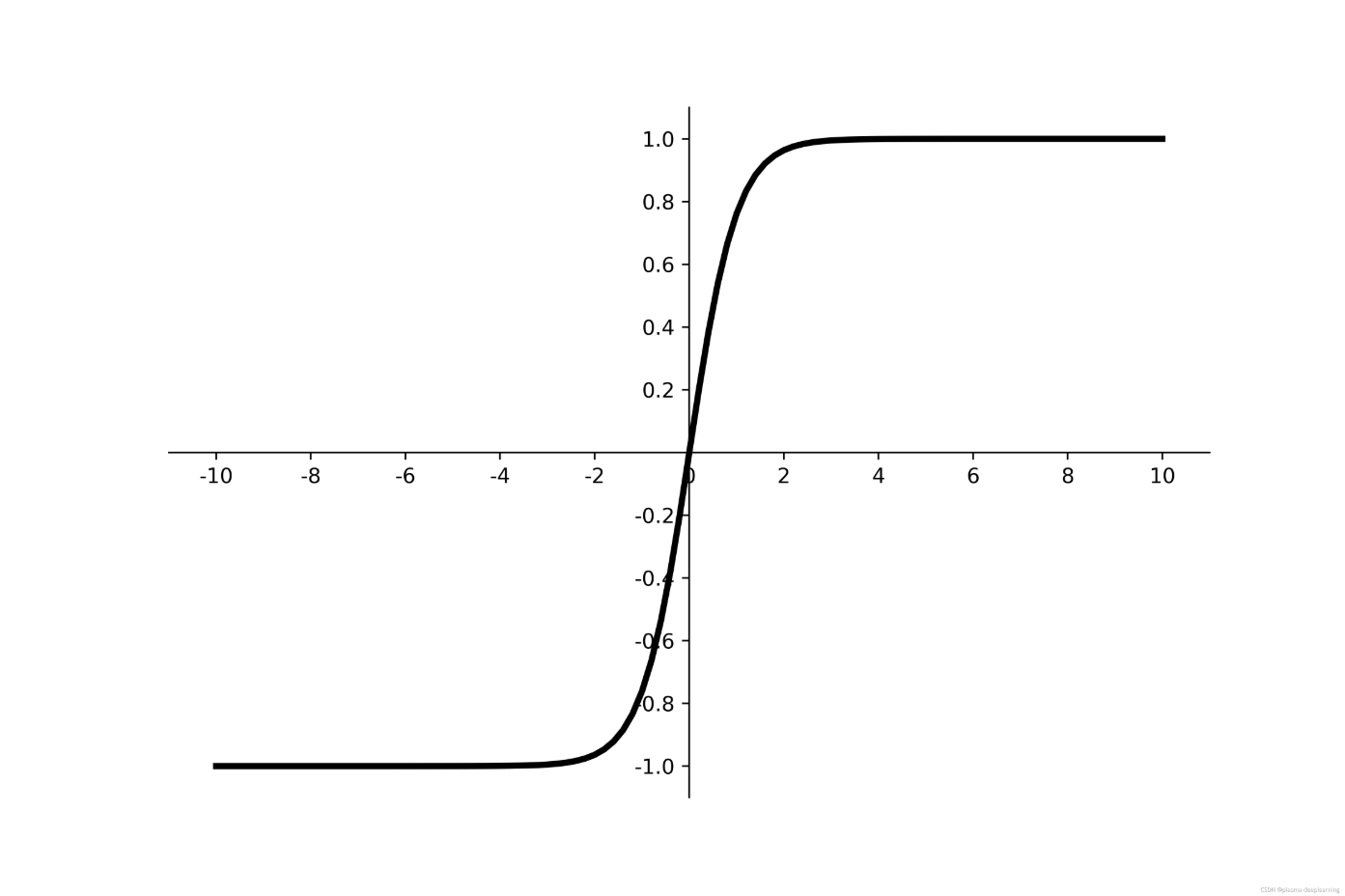
tanh
f(x) = (e^x - e^(-x)) / (e^x +e^(-x))
$$ f(x)=\frac{(ex-e{-x})} {e^x +e^{-x}} $$
取值范围为:(0,1)
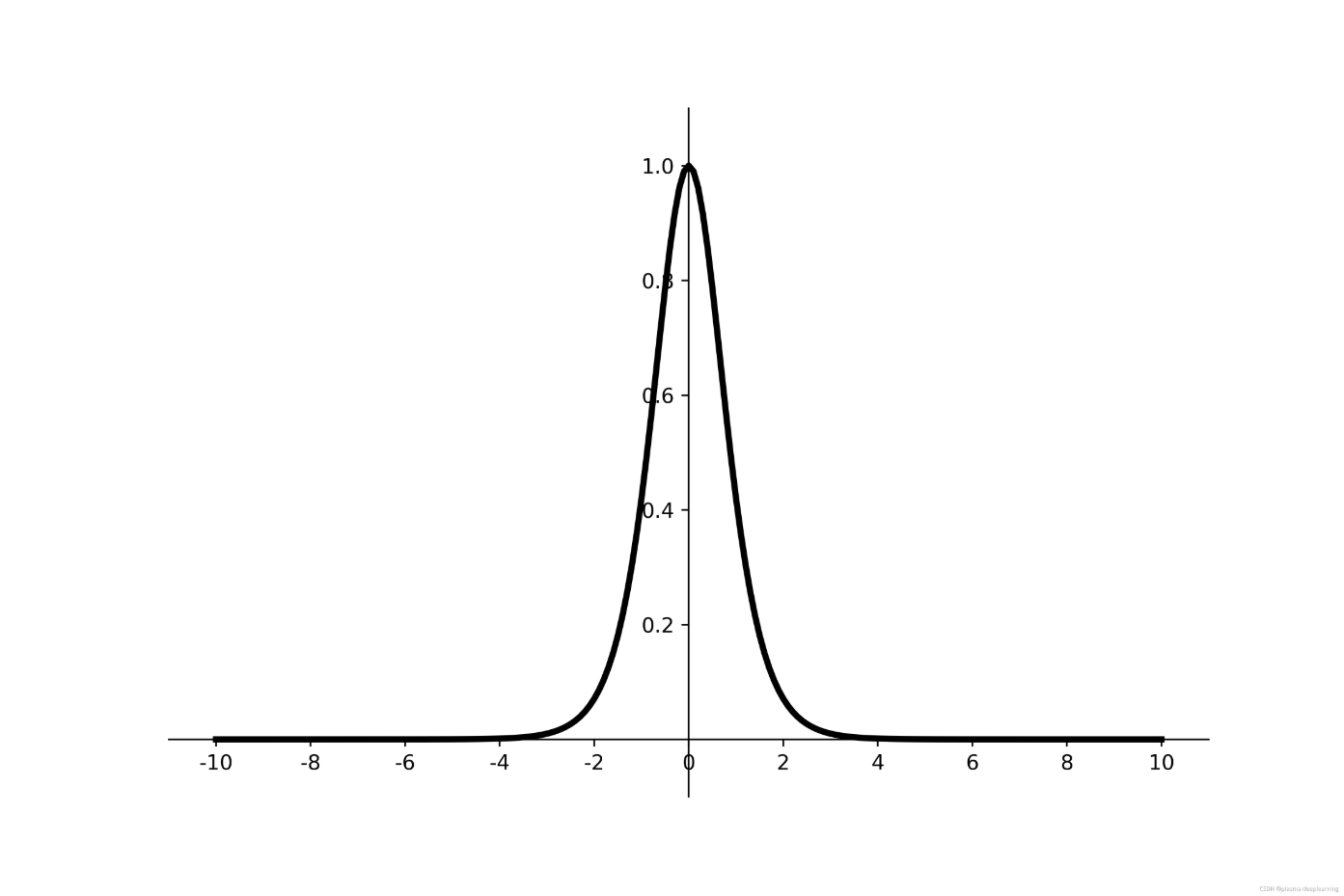
导数为:
f'(x) = 1 - f(x)^2
$$ f’(x) = 1 -f(x)^2 $$
优点:
- 比sigmoid函数收敛速度更快。
- 相比sigmoid函数,其输出以0为中心。
缺点:
- 易造成梯度消失;
- 幂运算复杂,训练时间长。
Softsign
f(x) = x/(1 + |x|)
取值范围: (-1,1)
f'(x) = 1/(1+x)^2
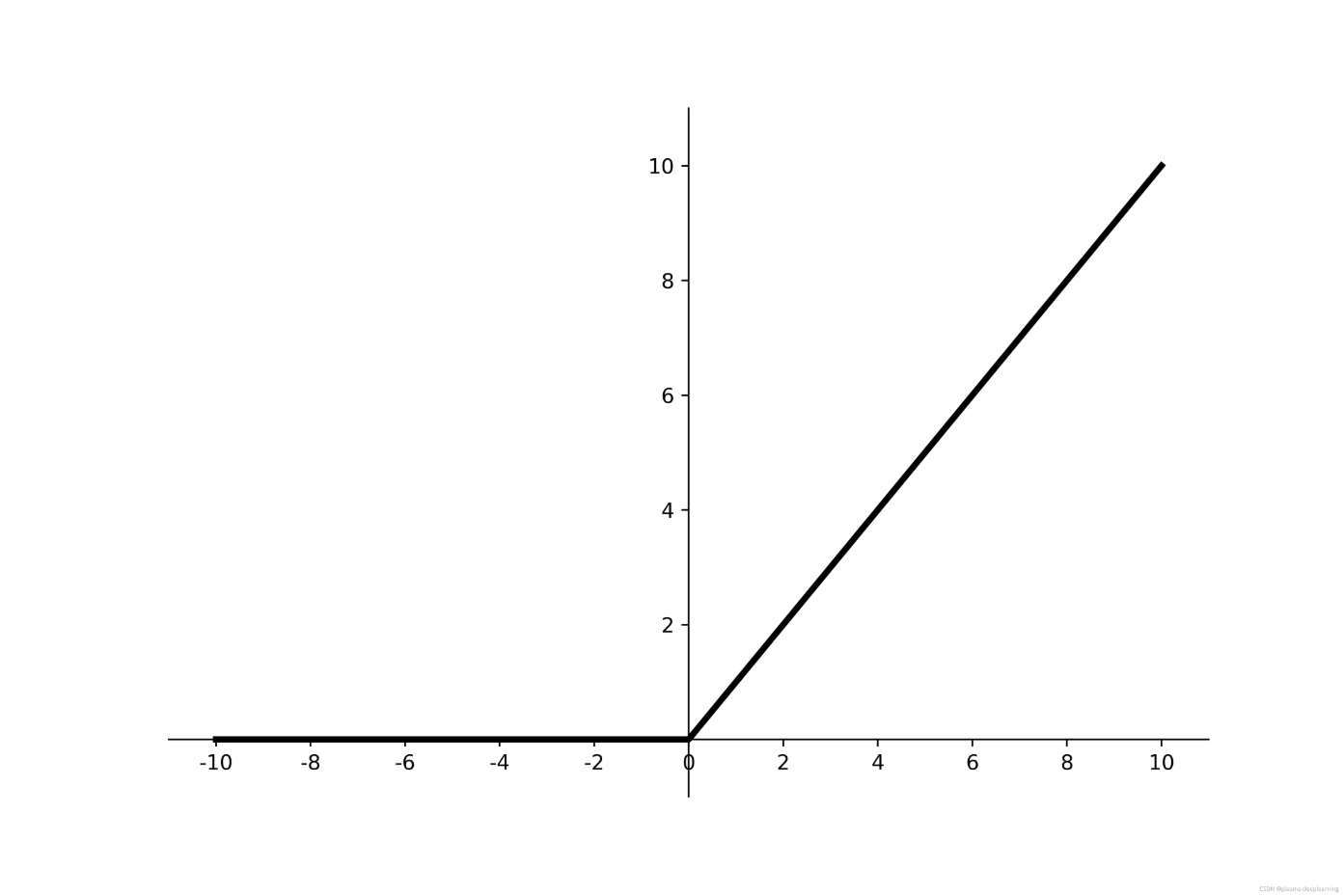
ReLU
f(x) = max(0,x)
$$ f(x) = \begin{cases} 0, & x < 0 \ x, & x \ge 0 \end{cases} $$
f(x)取值范围为 (0,+00)
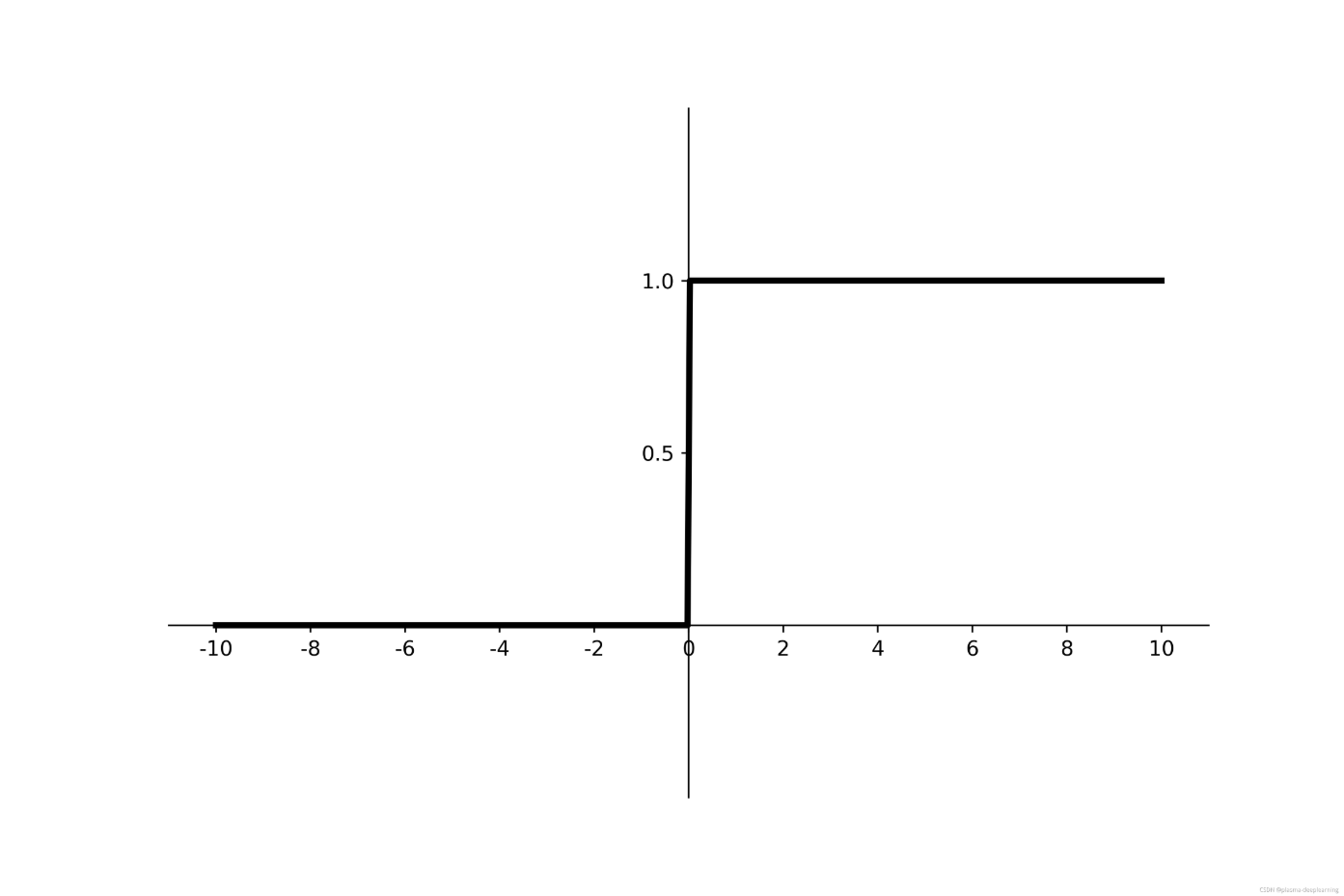
导数为:
f'(x) = max(0,1)
$$ f’(x)=max(0,1) $$
优点:
解决了梯度消失问题(在正区间); 只需判断输入是否大于0,计算速度快; 收敛速度远快于sigmoid和tanh,因为sigmoid和tanh涉及很多expensive的操作; 提供了神经网络的稀疏表达能力。
缺点:
输出非0均值,收敛慢; 神经元死亡:某些神经元可能永远不会被激活,导致相应的参数永远不能被更新。
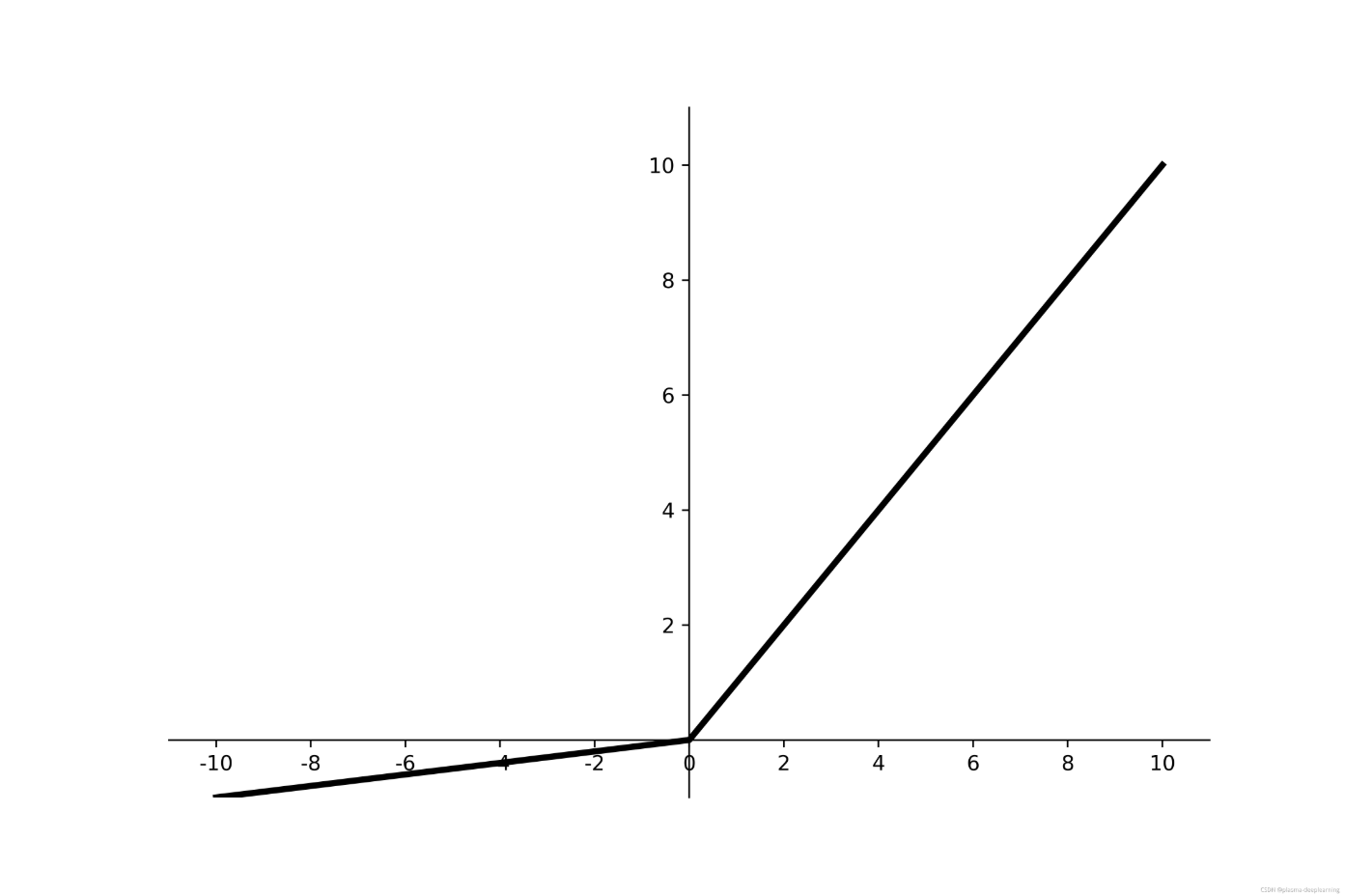
Leaky-ReLU
if x >= 0:
f(x) = x ;
if x < 0:
f(x) = ax ;
取值范围 (-00,+00);P-ReLU则认为 a 也应当作为一个参数来学习,一般建议初始化为0.25。
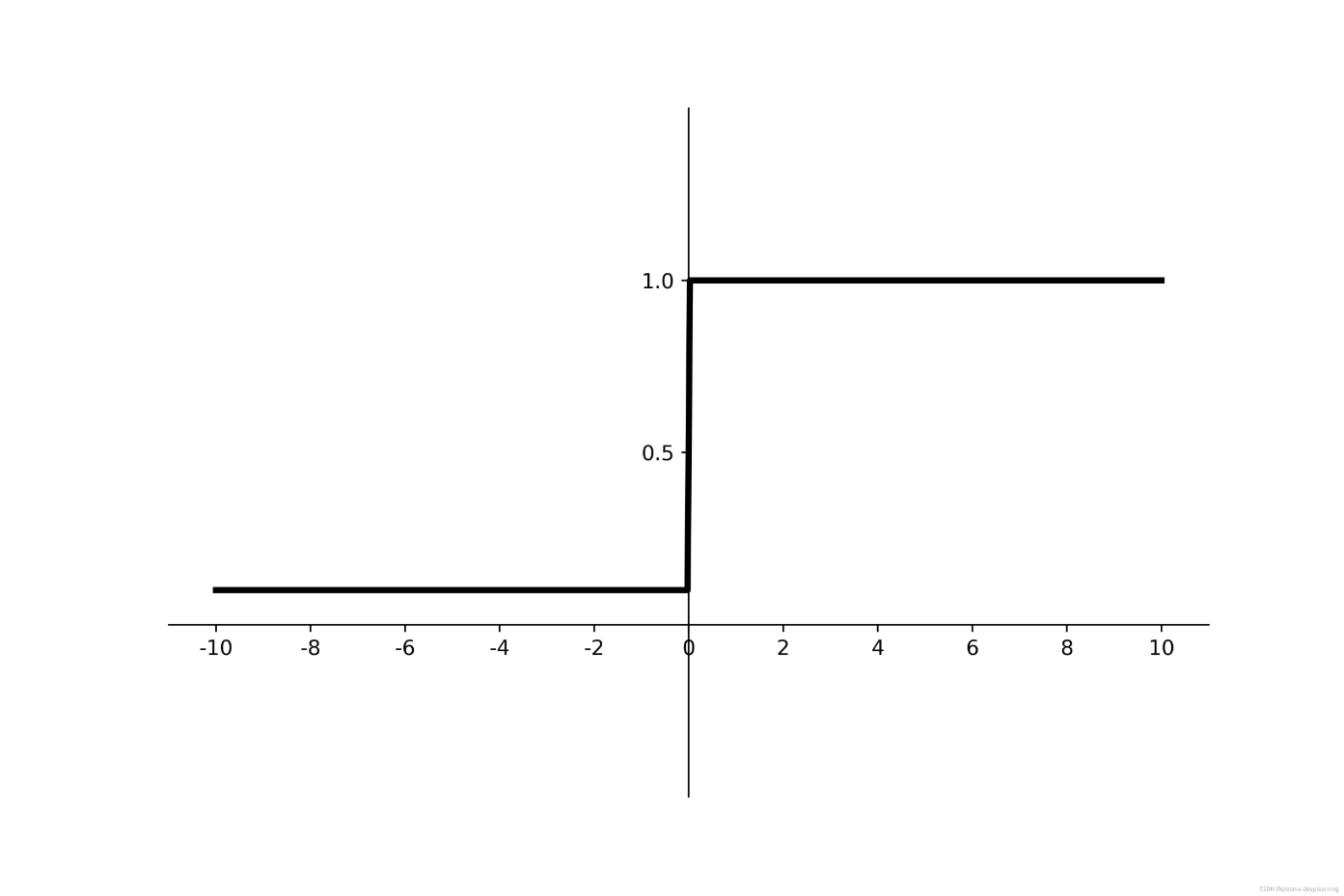
导数为:
if x >= 0;
f'(x) = 1 ;
if x <= 0;
f'(x) = a;
理论上来讲,Leaky ReLU有ReLU的所有优点,外加不会有神经元死亡的问题,但是在实际操作当中,并没有完全证明Leaky ReLU总是好于ReLU。
GeLU
原始公式 $$ \begin{equation} \mathrm{GELU}(x) = x \cdot \Phi(x) \
\text{其中} \space \Phi(x) = \frac{1}{2}\left[1 + \operatorname{erf}!\left(\frac{x}{\sqrt{2}}\right)\right]
\end{equation} $$
合并
$$ \begin{equation} \mathrm{GELU}(x)
x \cdot \frac{1}{2}\left[1 + \operatorname{erf}!\left(\frac{x}{\sqrt{2}}\right)\right] \end{equation} $$
但是实际的训练时使用的是近似的公式 $$ \begin{equation} \mathrm{GELU}(x)
\frac{x}{2} \left( 1 + \tanh \left( \sqrt{\frac{2}{\pi}} \left( x + 0.044715 x^{3} \right) \right) \right) \end{equation} $$
便是这样的情况
$$ \begin{align} \mathrm{GELU}(x) &= x \cdot \Phi(x) \ &= x \cdot \frac{1}{2}\left[1 + \operatorname{erf}!\left(\frac{x}{\sqrt{2}}\right)\right] \ &\approx \frac{x}{2}\left(1 + \tanh\left(\sqrt{\frac{2}{\pi}}\left(x + 0.044715 x^{3}\right)\right)\right) \end{align} $$
SwiGLU
$$
$$
ELU
if x >= 0:
f(x) = x;
if x < 0:
f(x) = a(e^x - 1);
$$ \text{ELU}(x) = \begin{cases} x, & x \ge 0 \ \alpha \left(e^x - 1\right), & x < 0 \end{cases} $$
Softmax
公式为:
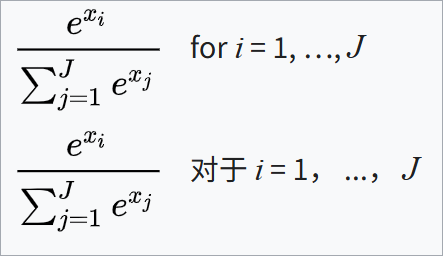
- 矩阵形式
$$ \text{Softmax}(\mathbf{z}) = \frac{e{\mathbf{z}}}{\sum_{j=1}{n} e^{z_j}} $$
损失函数
均方误差损失函数 MSE
MSE, Mean Squared Error
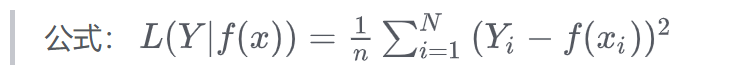
$$ L(Y|f(x))=\frac{1}{n}\sum_{i=1}{N} (Y_i-f(x_i))^2 $$
- pytorch 使用
import torch
y = torch
交叉熵损失 CrossEntropyLoss
总的函数 $$ L = -\sum_{i=1}^{n} y_i \log(\hat{y}_i) $$
- 单样本交叉熵
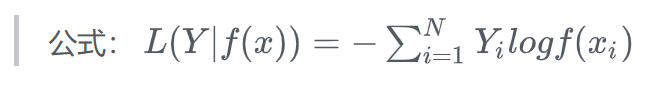
$$ L = -\sum_{i=1}^{n} y_i \log(\hat{y}_i) $$
- 多样本平均损失
$$ L = -\frac{1}{m}\sum_{k=1}{m}\sum_{i=1}{n} y_{k,i}\log(\hat{y}_{k,i}) $$
L1 损失
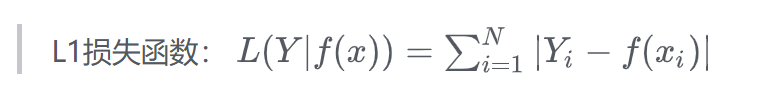
L2 损失
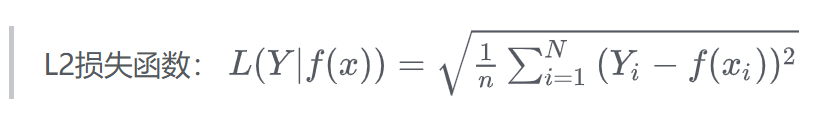
KL散度
KL 散度(Kullback–Leibler Divergence)
应用场景:VAE(变分自编码器)中衡量分布差异。
解释:越小代表两个分布越接近。 $$ D_{KL}(P|Q) = \sum_i P(i) \log \frac{P(i)}{Q(i)} $$